An in-depth comparison of Wi-Fi 7, Wi-Fi 6, and Wi-Fi 6E performance. Learn about the real-world speed, coverage, and reliability differences between these Wi-Fi standards.
Table of Contents
The Evolution of Wi-Fi: From Wi-Fi 1 to Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi technology has come a long way since its inception. The speed increase from the first version of Wi-Fi to the new Wi-Fi 7 standard is truly remarkable – a staggering 4,000 times faster. Even the jump from Wi-Fi 6 to Wi-Fi 7 represents a 5x increase in speed. To put this in perspective, imagine if cars had become five times faster in just the last 3 years. It’s an incredible rate of technological progress.
However, the latest and greatest Wi-Fi 7 systems come at a premium price point. And the assumption that Wi-Fi 7 will automatically provide better performance than Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t always true. This article will explore the real-world differences between these Wi-Fi standards when it comes to speed, reliability, and coverage.
Understanding Wi-Fi Basics
Before diving into the performance comparisons, it’s helpful to understand some Wi-Fi fundamentals:
- Wi-Fi uses radio waves at specific frequencies (like 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz) to transmit data wirelessly
- The radio waves carry digital information (1s and 0s) between devices
- Wi-Fi doesn’t provide internet access on its own – you need an internet service provider (ISP) and modem for that
- Wi-Fi creates a local area network (LAN) in your home to connect devices
- Wi-Fi standards (like Wi-Fi 6, 6E, 7) define the capabilities and protocols used
Key Wi-Fi Concepts
- Frequencies: The radio frequency bands used (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz)
- Channels: Smaller frequency ranges within each band
- Channel bandwidth: How wide each channel is (affects speed)
- MIMO: Multiple-input, multiple-output – allows simultaneous data streams
- QAM: Quadrature amplitude modulation – affects data density
Wi-Fi 6 vs 6E vs 7: Key Differences
Let’s examine how Wi-Fi 6, 6E, and 7 compare in terms of key capabilities:
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
- Wi-Fi 6: 9.6 Gbps
- Wi-Fi 6E: 9.6 Gbps
- Wi-Fi 7: 46 Gbps
Available Frequency Bands
- Wi-Fi 6: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz
- Wi-Fi 6E: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz
- Wi-Fi 7: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz
Maximum Channel Bandwidth
- Wi-Fi 6: 160 MHz
- Wi-Fi 6E: 160 MHz
- Wi-Fi 7: 320 MHz
Simultaneous Data Streams (MIMO)
- Wi-Fi 6: 8 streams
- Wi-Fi 6E: 8 streams
- Wi-Fi 7: Up to 16 streams
Data Density (QAM)
- Wi-Fi 6: 1024-QAM
- Wi-Fi 6E: 1024-QAM
- Wi-Fi 7: 4096-QAM
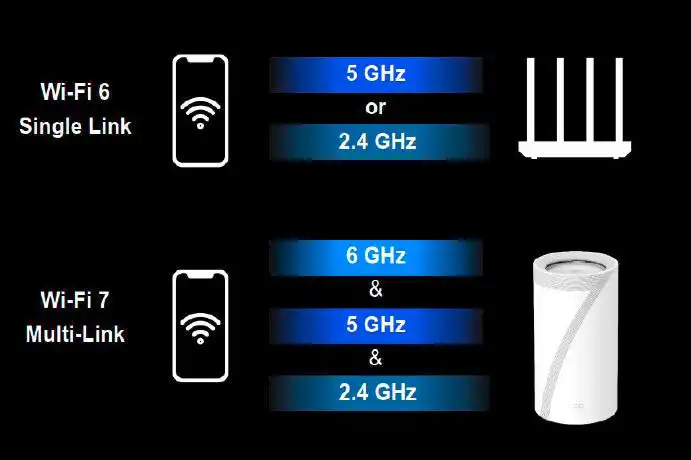
Multi-Link Operation (MLO)
- Wi-Fi 6: Not supported
- Wi-Fi 6E: Not supported
- Wi-Fi 7: Supported
Also Read :Top 5 SIM-Supported Wi-Fi Routers for Seamless Connectivity
Real-World Performance Testing
To compare the real-world performance of these Wi-Fi standards, extensive testing was conducted using TP-Link Wi-Fi systems in a 600 sq ft home environment. The testing focused on three key aspects:
- Speed
- Reliability
- Coverage
Speed Test Results
When comparing average speeds across the home:
- Wi-Fi 5 to Wi-Fi 7 showed clear speed improvements
- Wi-Fi 6E wasn’t consistently faster than Wi-Fi 6
- Wi-Fi 7 provided the highest speeds overall
However, maximum speeds were limited by the 960 Mbps internet plan used for testing. Internal network speeds (not relying on internet connection) showed 3-5x faster performance with Wi-Fi 7.
Why Wi-Fi 6E Wasn’t Always Faster
Wi-Fi 6E uses the 6 GHz band, which provides excellent speed but has more limited range. When averaging speeds across the entire home, this resulted in lower overall numbers for 6E. Within 15 feet of the router, 6E outperformed Wi-Fi 6.
Wi-Fi 7’s Speed Advantage
Wi-Fi 7 performed significantly better due to:
- Wider channel bandwidth (up to 320 MHz)
- Higher data density (4096-QAM)
- More simultaneous data streams (up to 16)
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO) – using multiple frequency bands simultaneously
Coverage Test Results
Coverage was primarily impacted by the frequency band used, rather than the Wi-Fi standard:
- 2.4 GHz provided the best range
- 5 GHz had moderate range
- 6 GHz had the shortest range
Signal strength measurements showed:
- 6 GHz signals dropped off faster than 5 GHz
- Usable 6 GHz coverage extended about 25 feet from the router
- Materials in the home significantly impact higher frequency signals
Reliability Factors
Several factors contribute to Wi-Fi reliability:
- Quality of the Wi-Fi system: Both TP-Link systems tested proved highly reliable over 3 months of use with 100+ connected devices.
- Processing power and radios: Wi-Fi routers need significant resources to manage connections and data streams.
- Device capacity: The tested TP-Link systems support up to 200 connected devices.
- Concurrent data streams: Wi-Fi 7 supports up to 16 simultaneous streams, reducing bottlenecks.
- Frequency balancing: Using 6 GHz for high-bandwidth devices frees up 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz for other connections.
- Backhaul method: Using wired backhaul between mesh points improves overall network performance.
Is Upgrading to Wi-Fi 6E or Wi-Fi 7 Worth It?
Based on the test results and real-world experience:
- Upgrading from Wi-Fi 6 to 6E or 7 is recommended for most users
- Wi-Fi 6E provides significant benefits at a lower cost than Wi-Fi 7
- Wi-Fi 7 offers the best performance but comes at a premium price
Reasons to Consider Wi-Fi 6E
- Access to the 6 GHz band for reduced interference
- Improved network balancing capabilities
- Better performance for streaming and high-bandwidth devices
- More affordable than Wi-Fi 7
Reasons to Consider Wi-Fi 7
- Fastest speeds available, especially for internal network transfers
- Best support for large numbers of connected devices
- Multi-Link Operation for optimized performance
- Future-proofing your network for upcoming devices and applications
Conclusion
Wi-Fi technology continues to evolve rapidly, with each new standard bringing significant improvements in speed, reliability, and overall performance. While Wi-Fi 7 currently offers the best performance, it comes at a premium price point. For many users, Wi-Fi 6E strikes a good balance between improved capabilities and cost.
When deciding whether to upgrade your Wi-Fi system, consider factors such as:
- The number of devices in your home
- Your internet service plan speed
- The types of activities you perform (streaming, gaming, file transfers, etc.)
- Your budget
Regardless of which standard you choose, investing in a quality Wi-Fi system from a reputable manufacturer like TP-Link can significantly improve your home network experience. As smart home technology continues to advance, having a robust and reliable Wi-Fi network will become increasingly important for managing and enjoying your connected devices.
Image credit: pcworld